At their core, AI chatbots are a blend of various technologies, chiefly natural language processing (NLP), machine learning (ML), and often deep learning. These technologies empower chatbots to understand, process, and respond to human language in a way that feels intuitive and contextually relevant.
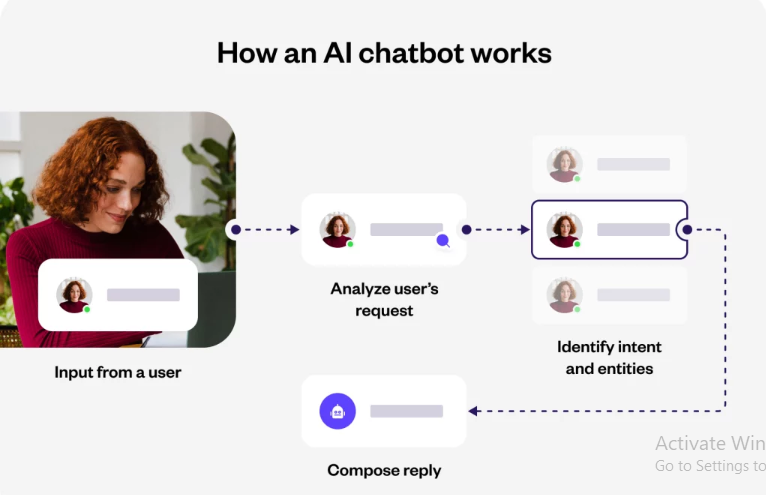
- Natural Language Processing (NLP): At the heart of AI recruiting lies Natural Language Processing (NLP), enabling chatbots to comprehend and respond to human language intricacies. In the recruitment realm, NLP dissects job descriptions, candidate resumes, and communication nuances.
- Machine Learning (ML) and Deep Learning (DL): Machine Learning empowers AI recruiters to learn and evolve from past interactions, while Deep Learning, a subset of ML, enhances decision-making through neural network simulations. With every interaction, AI recruiters fine-tune their responses to match evolving user needs. For example, when addressing recurrent inquiries about specific job features, an AI recruiter adapts by providing more detailed information, ensuring a personalized candidate experience.
- Integration with databases and systems: AI recruiters seamlessly integrate with databases and business systems, accessing relevant information and executing tasks. From sourcing candidates to managing applicant data, these integrations ensure streamlined recruitment processes. For instance, an AI recruiter integrated with a CRM system recognizes returning candidates, tailoring interactions based on past applications and preferences, fostering meaningful candidate relationships.
- Sentiment Analysis: Advanced AI recruiters employ sentiment analysis to gauge user emotions, allowing for empathetic and context-sensitive responses. For example, when detecting candidate frustration, an AI recruiter may offer empathetic reassurance or escalate concerns to human recruiters for personalized assistance, enhancing candidate satisfaction and engagement.
- Predictive Analytics and Decision-Making: AI recruiters leverage predictive analytics to anticipate candidate needs and offer proactive support. By analyzing candidate behaviors and preferences, they make informed recommendations, streamlining the recruitment journey. For instance, an AI recruiter may analyze candidate engagement patterns to predict potential job interests, suggesting relevant opportunities and enhancing candidate satisfaction.
- Human Oversight and Continuous Learning: AI recruiters operate under human oversight, ensuring continuous learning and adaptation. Regular review and feedback from recruitment teams keep AI models updated and aligned with company goals and policies. For example, a dedicated team monitors AI recruiter interactions, providing feedback and updates to ensure accurate and effective candidate engagement.



